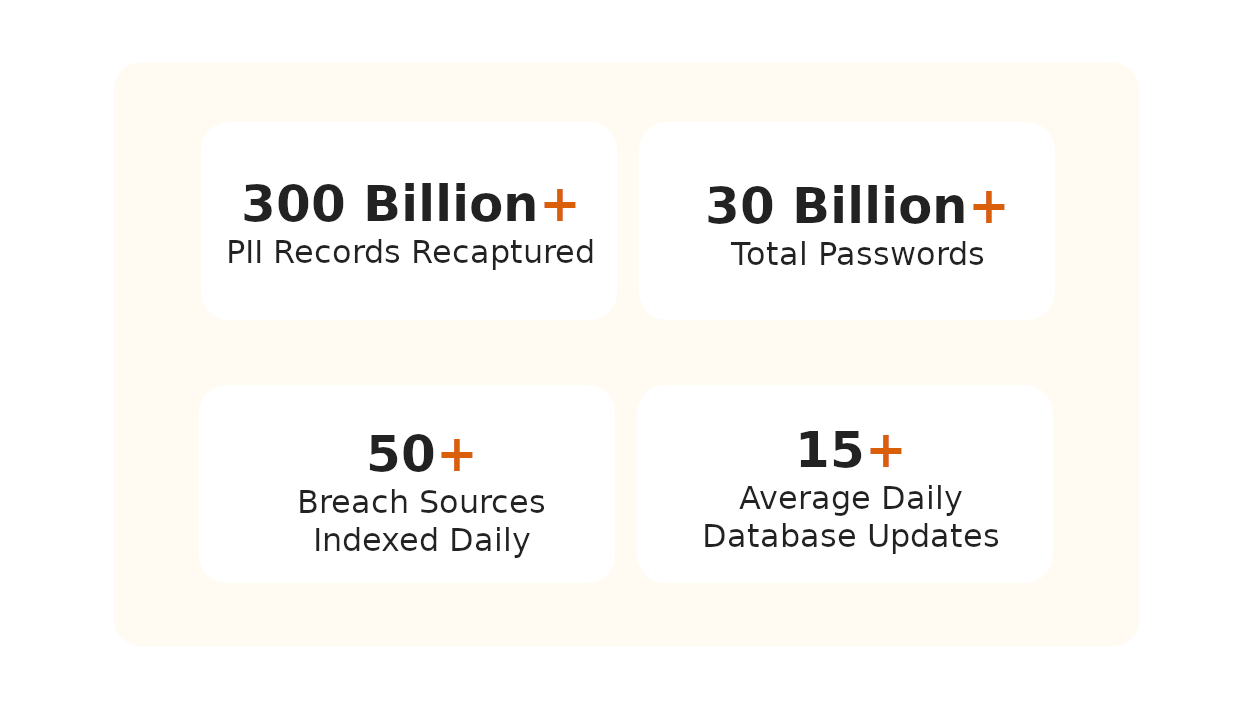
What is Leaked Credentials Monitoring?
How Credentials Get Leaked:
• Infostealer Malware: Malware like RedLine and Vidar infects employee devices and harvests saved passwords from browsers. We index these stealer logs within hours of exposure.
• Third-Party Breaches: When vendors get breached, your data ends up in the dump. Search leaked files for credentials linked to your organization.
• Ransomware Attacks: Attackers breach vendors and publish stolen data on leak sites. Our full-text search finds your company’s credentials in these files.
• Phishing Attacks: Credential harvesting campaigns trick employees into entering passwords on fake login pages.
Why Early Detection Matters:
Leaked credentials are exposed but not yet exploited. Compromised credentials are already being used by attackers. The difference is time. By detecting credentials when they’re leaked, you can reset them before they become compromised.
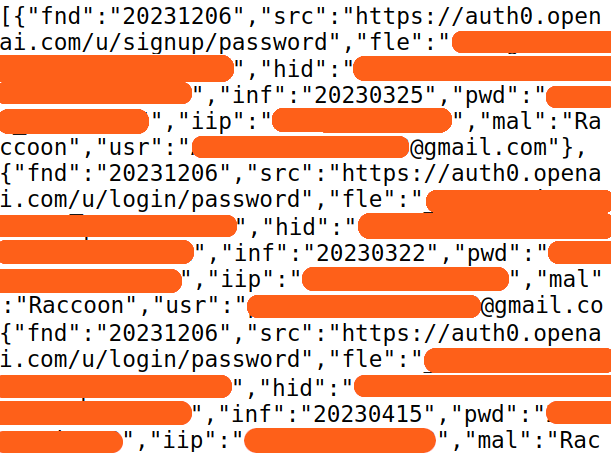
Full-Text Search on Leaked Files
Credentials From Stealer Logs
API-First for Security Teams
Trusted by Pen Testers, MSSPs, and Enterprise Security Teams
Our team uses Breachsense data to gain initial access during pen testing and red team engagements. The API is simple to use and the support is always helpful and responds quickly.
Our Security Colony platform relies on Breachsense data as part of our dark web monitoring service. The data is continuously updated and high quality. Highly recommend!
We rely on Breachsense for a lot of data. Their frequent database updates, constant availability, and handling of big and small breaches alike means we are always covered.
Leaked Credentials Resources
Protect your organization from credential-based attacks
Leaked Credentials Detection
Learn how to detect leaked credentials across dark web sources and stealer logs before attackers use them against you.
Learn MoreCheck If Employee Credentials Are Compromised
Step-by-step guide to checking if your employees’ credentials have been exposed in data breaches or infostealer logs.
Learn MoreWhat Are Compromised Credentials?
Understand how credentials become compromised and the difference between leaked, stolen, and actively exploited credentials.
Learn MoreHow to Prevent Credential Stuffing Attacks
Defense strategies against credential stuffing attacks that weaponize leaked username and password combinations.
Learn MoreHow to Prevent Password Spraying
Protect your organization from password spraying attacks that exploit common passwords across many accounts.
Learn MoreImpersonation Attack Examples
Real-world examples of impersonation attacks where attackers use leaked credentials to pose as legitimate users.
Learn MoreMalware Incident Response
How to respond when infostealer malware compromises employee devices and harvests credentials.
Learn MoreCurrent Malware Trends
Latest trends in credential-stealing malware including infostealers like RedLine and Vidar.
Learn MoreRansomware Attack Response Plan
Develop a response plan for ransomware attacks, which often begin with leaked or stolen credentials.
Learn MoreRansomware Trends
Current ransomware trends and how credential exposure connects to ransomware initial access.
Learn MoreLeaked Credentials Definition
Quick reference guide to understanding what leaked credentials are and why they matter.
Learn MoreCredential Harvesting Attacks
Learn how attackers harvest credentials through phishing, keyloggers, and other techniques.
Learn MoreFrequently Asked Questions
Leaked credentials are usernames and passwords exposed through data breaches or infostealer malware. Phishing attacks expose them too. They’ve been disclosed to unauthorized parties but may not yet be actively exploited. The goal of monitoring is to find them during this window before attackers weaponize them.
Credentials leak through multiple channels. Infostealer malware infects devices and harvests saved browser passwords. Third-party breaches expose credentials when vendors get hacked. Credential harvesting through phishing tricks users into entering passwords on fake sites. Once leaked, credentials end up in stealer logs and dark web marketplaces.
Leaked credentials monitoring scans dark web marketplaces and infostealer logs for exposed login credentials linked to your organization. It also covers third-party breach data and criminal forums. According to Verizon’s DBIR, stolen credentials are involved in most breaches. When employee passwords appear in these sources, you get an alert so you can reset them before attackers exploit them.
Because credentials leak constantly and attackers move fast. IBM X-Force 2025 reports an 84% increase in phishing emails delivering infostealers. These infections harvest passwords from employee devices and dump them into stealer log channels within hours. Without monitoring, you won’t know credentials are exposed until attackers use them for account takeover or lateral movement.
Act fast. Reset the exposed passwords immediately and terminate any active sessions for affected accounts. Check for signs of unauthorized access or suspicious activity. If the credentials were harvested by infostealer malware, the infected device needs to be isolated and remediated. Finally, notify affected users and enforce a password change.
Leaked credentials are exposed but not necessarily being used by attackers yet. Compromised credentials are actively being exploited. Think of it as a timeline: credentials get leaked first, then attackers find them, then they become compromised. Leaked credentials monitoring catches them early in this timeline, while compromised credential monitoring detects active exploitation.